Progesterone, a vital reproductive hormone, plays a crucial role in pregnancy and offers a multitude of benefits for a woman’s overall health and well-being. While low progesterone levels can impact fertility and increase the risk of miscarriage, understanding your progesterone levels is essential for every woman, irrespective of her desire to conceive. In this blog post, we will delve into the various functions of progesterone, highlighting its significance beyond pregnancy.
Maintaining a Healthy Uterine Lining: Progesterone plays a pivotal role in preparing the uterine lining for implantation. Adequate progesterone levels ensure that the endometrium is properly nourished and can support a fertilized egg, increasing the chances of successful implantation and pregnancy.
Managing PMS & PMDD Symptoms: Progesterone helps alleviate the symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Its balancing effect on hormones can reduce mood swings, irritability, bloating, and breast tenderness, providing relief and promoting emotional well-being during the menstrual cycle.
Enhancing Mental Health & Sleep: Progesterone has a positive impact on mental health, contributing to improved mood and reduced anxiety. It also supports healthy sleep patterns, aiding in better quality rest and overall well-being.
Promoting Brain & Heart Health: Studies suggest that progesterone is beneficial for brain health, with potential neuroprotective effects. It may enhance cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health. Additionally, progesterone contributes to cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure and blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Protecting Against Cancers & Reproductive Disorders: Progesterone exhibits protective properties against various cancers, including breast and uterine cancers. It also helps prevent fibrocystic disease and ovarian cysts, reducing the risk of reproductive health issues.
Stress Management & Metabolism Support: Progesterone increases the body’s ability to handle stress and may have a positive impact on the metabolism. It assists in the utilization of fat for energy, contributing to weight management and overall metabolic health.
Bone Health & Aging: Progesterone is essential for bone growth and helps prevent osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. Additionally, progesterone’s influence on hormone balance and its potential anti-aging effects contribute to overall well-being.
Improving Libido & Reducing Migraines: Progesterone can enhance libido and improve sexual well-being. It may also reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines, providing relief for those who experience these debilitating headaches.
Reducing Inflammation & Joint Pain: Progesterone exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, potentially reducing inflammation and joint pain. This benefit can be particularly significant for women experiencing conditions such as arthritis or general joint discomfort.
Progesterone plays a vital role in reproductive health, pregnancy, and overall well-being for women. Its effects extend beyond fertility and have a profound impact on mental health, sleep, heart health, bone health, aging, and various other aspects of a woman’s life. Monitoring progesterone levels and seeking appropriate support is crucial for optimal health and hormone balance.
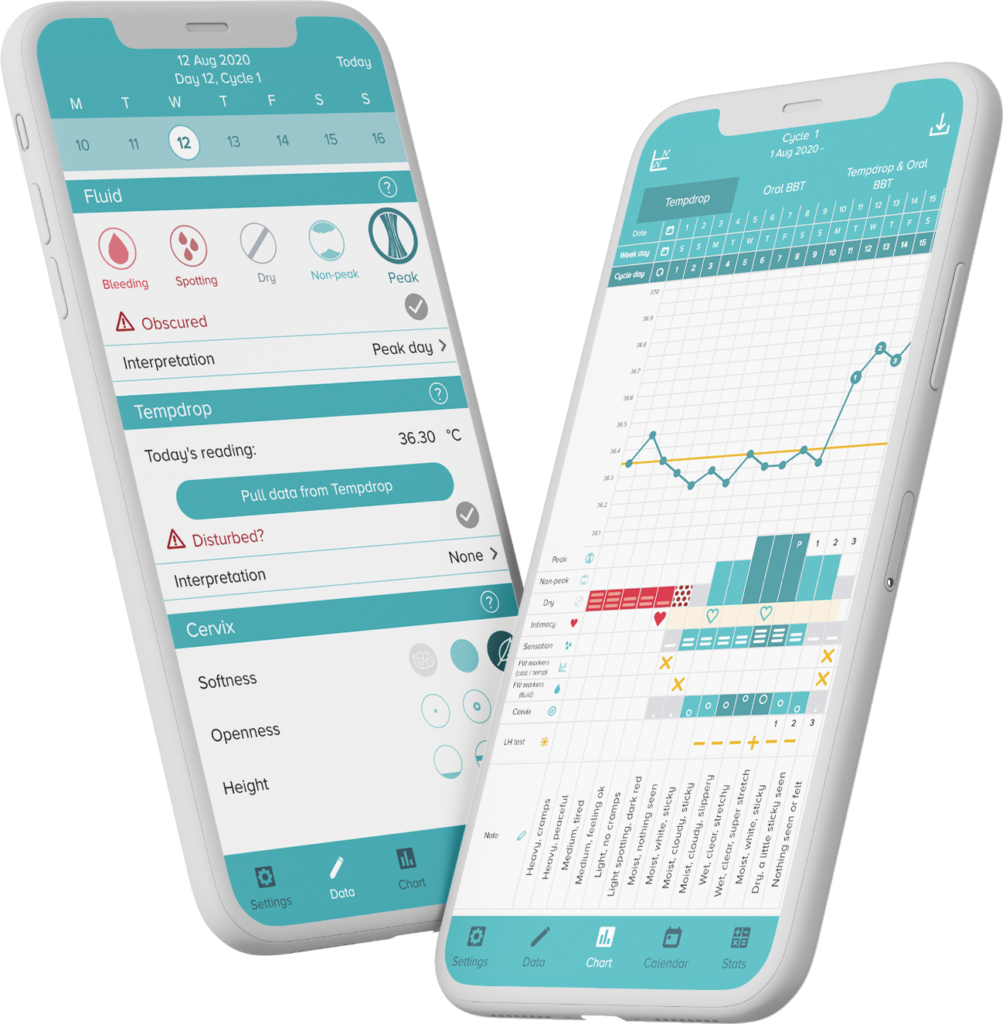
The great news is, monitoring for signs of low progesterone is pretty simple when charting your cycles with The Fertility Awareness Method, and for a concrete assessment of your levels, progesterone can be tested through a simple blood test from your GP or holistic health practitioner.
If you’re ready to take charge of your hormonal health and fertility, check out the programs tab on my website, or book in a free 30-minute fertility strategy call here.
References:
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2019). What are the benefits of progesterone? Retrieved from https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/what-are-the-benefits-of-progesterone
- Velez, M. P., & Arbuckle, T. E. (2020). Progesterone and premenstrual syndrome: A systematic review. Frontiers in